|
|
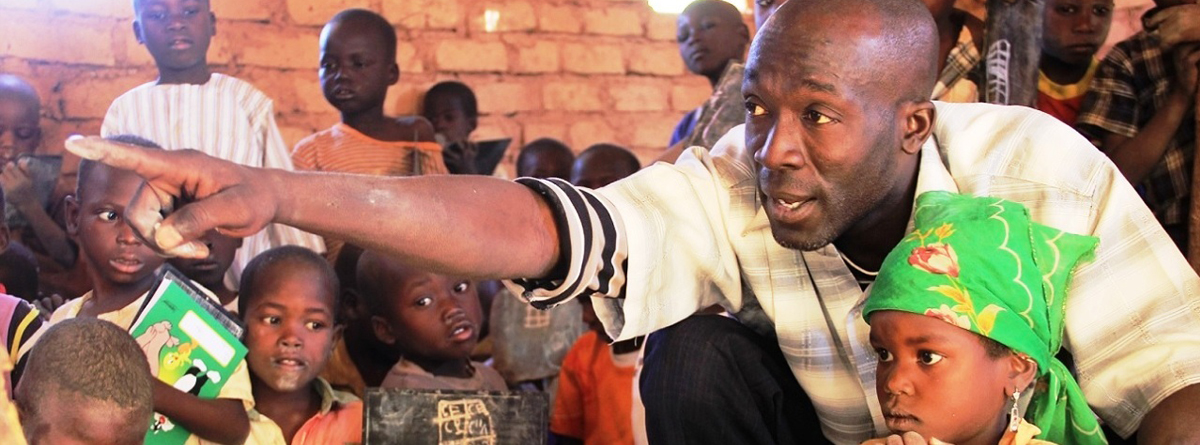
Algeria
Chicago – Bridgeview



Profile
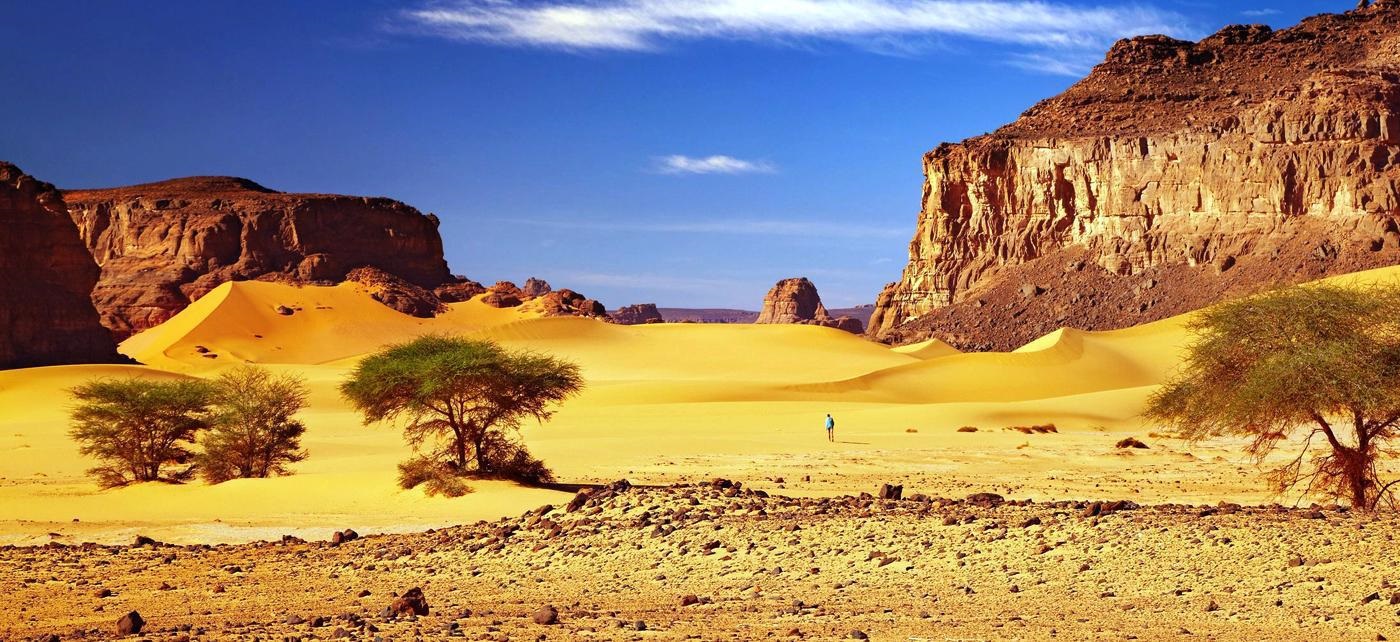
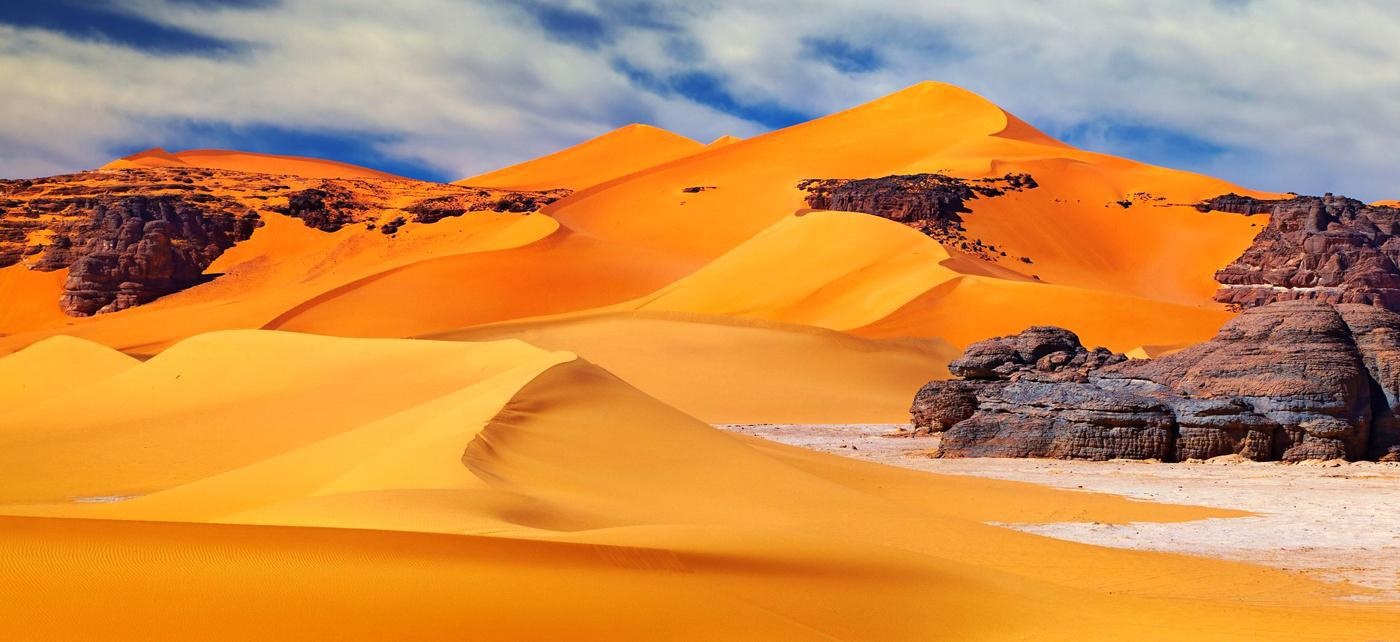
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb. In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa, the Arab World and the Mediterranean Sea followed by Democratic Republic of Congo, thus more than 90% of its surface is covered by the Sahara desert. Overall, it is the 10th-largest country in the world.
Algeria is bordered in the northeast by Tunisia, in the east by Libya, in the west by Morocco, in the southwest by Western Sahara, Mauritania, and Mali, in the southeast by Niger, and in the north by the Mediterranean Sea. Its size is almost 2,400,000 square kilometers (926,645 sq mi), and it has an estimated population of 35.7 million (2010). The capital of Algeria is Algiers. Algeria is a member of the Arab League, United Nations, African Union, and OPEC. It is also a founding member of the Arab Maghreb Union.
In Antiquity Algeria was known as the kingdom of Numidia and its people were called the Numidians. The kingdom of Numidia had early relations with the Carthaginians, Romans and Ancient Greeks, the region was considered a fertile area, and the Numidians were known for their fine cavalry. The indigenous peoples of northern Africa eventually coalesced into a distinct native population, the Berbers. After 1000 BCE, the Carthaginians began establishing settlements along the coast. The Berbers seized the opportunity offered by the Punic Wars to become independent of Carthage, and Berber kingdoms began to emerge, most notably Numidia.
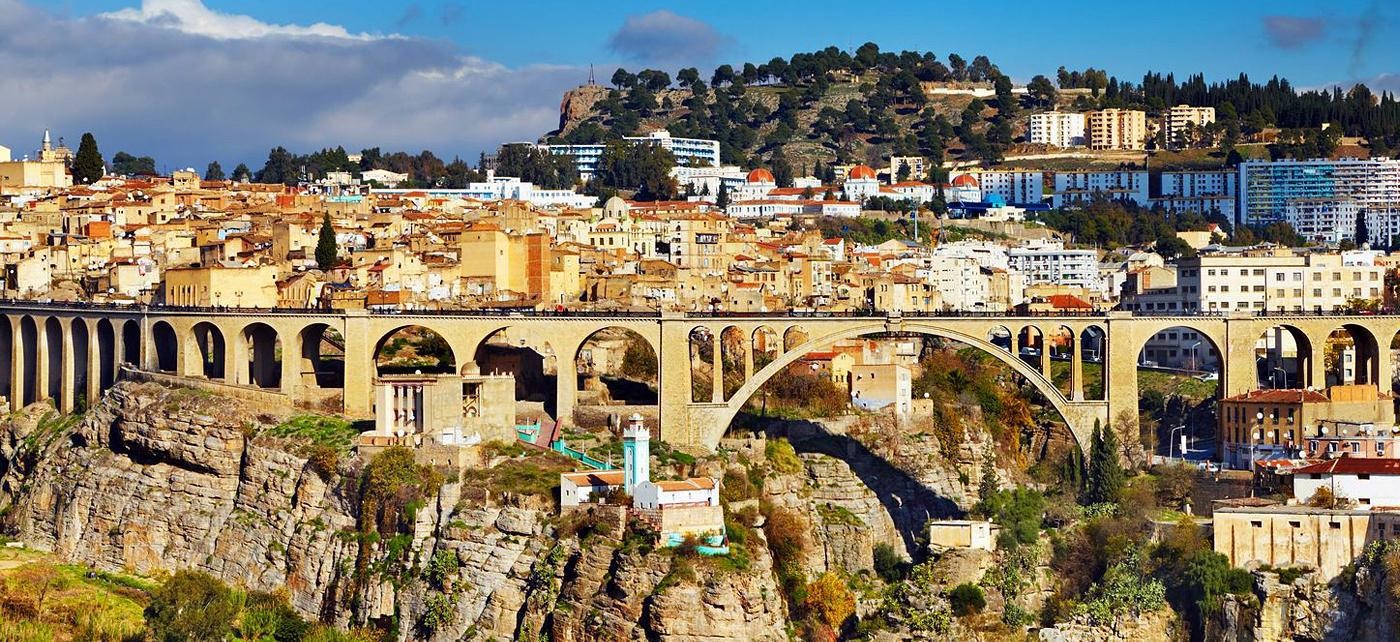
Algeria lies mostly between latitudes 19° and 37°N (a small area is north of 37°), and longitudes 9°W and 12°E. Most of the coastal area is hilly, sometimes even mountainous, and there are a few natural harbours. The area from the coast to the Tell Atlas is fertile. South of the Tell Atlas is a steppe landscape, which ends with the Saharan Atlas; further south, there is the Sahara desert. The Ahaggar Mountains, also known as the Hoggar, are a highland region in central Sahara, southern Algeria. They are located about 1,500 km (932 mi) south of the capital, Algiers and just west of Tamanghasset. Algiers, Oran, Constantine, Tizi Ouzou and Annaba are Algeria's main cities.
Algeria has always been noted for the fertility of its soil. 25% of Algerians are employed in the agricultural sector. A considerable amount of cotton was grown at the time of the United States' Civil War, but the industry declined afterwards. In the early years of the 20th century efforts to extend the cultivation of the plant were renewed. A small amount of cotton is also grown in the southern oases. Large quantities of dwarf palm are cultivated for the leaves, the fibers of which resemble horsehair. The olive (both for its fruit and oil) and tobacco are cultivated with great success.
More than 30,000 km2 (7,000,000 acres) are devoted to the cultivation of cereal grains. The Tell Atlas is the grain-growing land. During the time of French rule its productivity was increased substantially by the sinking of artesian wells in districts which only required water to make them fertile. Of the crops raised, wheat, barley and oats are the principal cereals. A great variety of vegetables and fruits, especially citrus products, are exported. Algeria also exports figs, dates, esparto grass, and cork. It is the largest oat market in Africa.
Algeria is bordered in the northeast by Tunisia, in the east by Libya, in the west by Morocco, in the southwest by Western Sahara, Mauritania, and Mali, in the southeast by Niger, and in the north by the Mediterranean Sea. Its size is almost 2,400,000 square kilometers (926,645 sq mi), and it has an estimated population of 35.7 million (2010). The capital of Algeria is Algiers. Algeria is a member of the Arab League, United Nations, African Union, and OPEC. It is also a founding member of the Arab Maghreb Union.
In Antiquity Algeria was known as the kingdom of Numidia and its people were called the Numidians. The kingdom of Numidia had early relations with the Carthaginians, Romans and Ancient Greeks, the region was considered a fertile area, and the Numidians were known for their fine cavalry. The indigenous peoples of northern Africa eventually coalesced into a distinct native population, the Berbers. After 1000 BCE, the Carthaginians began establishing settlements along the coast. The Berbers seized the opportunity offered by the Punic Wars to become independent of Carthage, and Berber kingdoms began to emerge, most notably Numidia.
Algeria lies mostly between latitudes 19° and 37°N (a small area is north of 37°), and longitudes 9°W and 12°E. Most of the coastal area is hilly, sometimes even mountainous, and there are a few natural harbours. The area from the coast to the Tell Atlas is fertile. South of the Tell Atlas is a steppe landscape, which ends with the Saharan Atlas; further south, there is the Sahara desert. The Ahaggar Mountains, also known as the Hoggar, are a highland region in central Sahara, southern Algeria. They are located about 1,500 km (932 mi) south of the capital, Algiers and just west of Tamanghasset. Algiers, Oran, Constantine, Tizi Ouzou and Annaba are Algeria's main cities.
Algeria has always been noted for the fertility of its soil. 25% of Algerians are employed in the agricultural sector. A considerable amount of cotton was grown at the time of the United States' Civil War, but the industry declined afterwards. In the early years of the 20th century efforts to extend the cultivation of the plant were renewed. A small amount of cotton is also grown in the southern oases. Large quantities of dwarf palm are cultivated for the leaves, the fibers of which resemble horsehair. The olive (both for its fruit and oil) and tobacco are cultivated with great success.
More than 30,000 km2 (7,000,000 acres) are devoted to the cultivation of cereal grains. The Tell Atlas is the grain-growing land. During the time of French rule its productivity was increased substantially by the sinking of artesian wells in districts which only required water to make them fertile. Of the crops raised, wheat, barley and oats are the principal cereals. A great variety of vegetables and fruits, especially citrus products, are exported. Algeria also exports figs, dates, esparto grass, and cork. It is the largest oat market in Africa.
Country Location